Breadcrumb
- Home
- Illnesses & Conditions
- Diabetes
- Diabetic Retinopathy
Content Map Terms
Illnesses & Conditions Categories
-
Allergies
- Allergy to Natural Rubber (Latex)
- Jellyfish Stings: Allergic Reaction
- Allergies: Should I Take Allergy Shots?
- Non-Allergic Rhinitis
- Allergic Reaction
- Allergies
- Allergy Shots for Allergic Rhinitis
- Allergies: Rush Immunotherapy
- Over-the-Counter Medicines for Allergies
- Allergic Rhinitis
- Allergic Rhinitis: Common Triggers
- Allergies: Avoiding Indoor Triggers
- Allergies: Avoiding Outdoor Triggers
- Controlling Dust, Dust Mites, and Other Allergens in Your Home
- Controlling Pet Allergens
- Allergies to Insect Stings
- Allergies: Should I Take Shots for Insect Sting Allergies?
- Immunotherapy for Allergies to Insect Stings
- Types of Allergic Rhinitis
- Allergic Reaction to Tattoo Dye
- Drug Allergies
- Penicillin Allergy
- Hay Fever and Other Seasonal Allergies
- Allergies: Giving Yourself an Epinephrine Shot
-
Arthritis and Osteoporosis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Finger and Hand Surgeries
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Classification Criteria
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Systemic Symptoms
- Comparing Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Neck Symptoms
- Osteoporosis in Men
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Arthritis: Shots for Knee Pain
- Complementary Medicine for Arthritis
- Steve's Story: Coping With Arthritis
- Bev's Story: Coping With Arthritis
- Quick Tips: Modifying Your Home and Work Area When You Have Arthritis
- Coping With Osteoarthritis
- Arthritis: Should I Have Shoulder Replacement Surgery?
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- Capsaicin for Osteoarthritis
- Small Joint Surgery for Osteoarthritis
- Osteoarthritis: Heat and Cold Therapy
- Modifying Activities for Osteoarthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Gout
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Inflammatory Eye Disease
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Range-of-Motion Exercises
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Deciding About Total Joint Replacement
- Complications of Osteoarthritis
- Arthritis: Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Arthritis: Should I Have Knee Replacement Surgery?
- Arthritis: Should I Have Hip Replacement Surgery?
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Pain Management
- Osteoporosis Risk in Younger Women
- Osteoporosis Screening
-
Asthma
- Asthma: Peak Expiratory Flow and Personal Best
- Asthma and Wheezing
- Asthma: Using an Asthma Action Plan
- Asthma: Measuring Peak Flow
- Asthma: Identifying Your Triggers
- Steroid Medicine for Asthma: Myths and Facts
- Asthma
- Inhaled corticosteroids for asthma
- Inhaled quick-relief medicines for asthma
- Classification of Asthma
- Challenge Tests for Asthma
- Asthma's Impact on Your Child's Life
- Asthma Action Plan: Yellow Zone
- Asthma Triggers
- Asthma Action Plan: Red Zone
- Asthma and GERD
- Occupational Asthma
- Asthma Attack
- Asthma: Symptoms of Difficulty Breathing
- Exercise-Induced Asthma
- Asthma Treatment Goals
- Asthma: Overcoming Obstacles to Taking Medicines
- Asthma in Older Adults: Managing Treatment
- Asthma: Controlling Cockroaches
- Asthma: Educating Yourself and Your Child
- Allergy Shots for Asthma
- Asthma: Taking Charge of Your Asthma
- Monitoring Asthma Treatment
- Omalizumab for Asthma
- Asthma: Ways to Take Inhaled Medicines
- Asthma: Overuse of Quick-Relief Medicines
- Asthma Diary
- Asthma Diary Template
- Asthma Action Plan
- Assessing Your Asthma Knowledge
-
Bowel and Gastrointestinal Conditions
- Abdominal Fullness or Bloating
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Criteria for Diagnosis
- Gastritis
- Gas, Bloating, and Burping
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Constipation: Keeping Your Bowels Healthy
- Rectal Problems
- Mild, Moderate, or Severe Diarrhea
- Torn or Detached Nail
- Chronic Constipation
- Gas (Flatus)
- Dyspepsia
- Diverticulosis
- Bowel Obstruction
- Anal Fissure
- Bowel Disease: Caring for Your Ostomy
- Anal Fistulas and Crohn's Disease
-
Cancer
- Lung Cancer and Other Lung Problems From Smoking
- Skin Cancer, Non-Melanoma
- Radiation Therapy for Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer Test Recommendations
- Breast Cancer Screening: When Should I Start Having Mammograms?
- Lifestyle Changes That May Help Prevent Cancer
- Choosing a Prosthesis After Breast Cancer Surgery
- Hormone Treatment for Breast Cancer
- Cancer Staging and Grading
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Kidney (Renal Cell) Cancer
- Cancer Support: Managing Stress
- Cancer Support: When Your Cancer Comes Back or Gets Worse
- Cancer Support: Dealing With Emotions and Fears
- Cancer Support: Finding Out That You Have Cancer
- Cancer Support: Being an Active Patient
- Cancer Support: Coping With Cancer Treatments
- Cancer Support: Life After Treatment
- Cancer Support: Family, Friends, and Relationships
- Reducing Cancer Risk When You Are BRCA-Positive
- Anal Cancer
- Prostate Cancer: Should I Choose Active Surveillance?
- Lung Cancer Screening
- Tumour Markers
- Does Aspirin Prevent Cancer?
- Cancer
- Lung Cancer
- Oral Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer
- Metastatic Melanoma
- Radiation Treatment for Cancer
- Skin Cancer, Melanoma
- Cervical Cancer Screening
- Hepatitis B and C: Risk of Liver Cancer
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) and Cancer Risk
- Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Cancer: Home Treatment for Mouth Sores
- Skin Cancer Screening
- Breast Cancer: Should I Have Breast Reconstruction After a Mastectomy?
- Prostate Cancer: Should I Have Radiation or Surgery for Localized Prostate Cancer?
- Prostate Cancer Screening
- Side Effects of Chemotherapy
- Breast Cancer: Lymph Node Surgery for Staging Cancer
- Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer
- Cryosurgery for Prostate Cancer
- Breast Cancer
- Cancer: Home Treatment for Nausea or Vomiting
- Cancer: Home Treatment for Pain
- Cancer: Home Treatment for Diarrhea
- Cancer: Home Treatment for Constipation
- Breast Cancer Types
- Cancer: Home Treatment for Sleep Problems
- Cancer: Home Treatment for Fatigue
- Hair Loss From Cancer Treatment
- Body Image After Cancer Treatment
- Breast Cancer: Should I Have Breast-Conserving Surgery or a Mastectomy for Early-Stage Cancer?
- Breast Cancer, Metastatic or Recurrent
- Cancer Pain
- Leukemia
- Colorectal Cancer, Metastatic or Recurrent
- Thyroid Cancer
- Types of Thyroid Cancer
- Radiation Therapy for Cancer Pain
- Breast Cancer in Men (Male Breast Cancer)
- Breast Cancer Screening
- Breast Cancer: Should I Have Chemotherapy for Early-Stage Breast Cancer?
- Asbestos and Lung Cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer Genetic Testing
- Testicular Cancer Screening
- Skin Cancer: Protecting Your Skin
- Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: Comparing Treatments
- Bladder Cancer
- Prostate Cancer, Advanced or Metastatic
- Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer
- Urinary Problems and Prostate Cancer
- Cancer: Controlling Cancer Pain
- Heat and Cold Treatment for Cancer Pain
- Testicular Cancer
- Cancer: Controlling Nausea and Vomiting From Chemotherapy
- Lymphedema: Managing Lymphedema
- Inflammatory Breast Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer: Should I Have My Ovaries Removed to Prevent Ovarian Cancer?
- Family History and the Risk for Breast or Ovarian Cancer
- Breast Cancer: What Should I Do if I'm at High Risk?
- Cold and Flu
-
COPD
- Cal's Story: Learning to Exercise When You have COPD
- Conserving Energy When You Have COPD or Other Chronic Conditions
- Nebulizer for COPD Treatment
- COPD Action Plan
- COPD: Help for Caregivers
- COPD: Keeping Your Diet Healthy
- COPD: Using Exercise to Feel Better
- COPD
- COPD Flare-Ups
- Bullectomy for COPD
- COPD and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (AAT) Deficiency
- COPD and Sex
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation
- COPD
- Oxygen Treatment for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- COPD: Avoiding Weight Loss
- COPD: Avoiding Your Triggers
-
Dementia
- Alzheimer's and Other Dementias: Coping With Sundowning
- Dementia: Assessing Pain
- Medical History and Physical Examination for Dementia or Alzheimer's Disease
- Alzheimer's and Other Dementias: Making the Most of Remaining Abilities
- Dementia: Helping a Person Avoid Confusion
- Alzheimer's and Other Dementias: Maintaining Good Nutrition
- Dementia: Tips for Communicating
- Agitation and Dementia
- Dementia: Bladder and Bowel Problems
- Dementia: Support for Caregivers
- Dementia: Legal Issues
- Dementia: Understanding Behaviour Changes
- Dementia: Medicines to Treat Behaviour Changes
- Dementia
- Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia
-
Diabetes
- Diabetes: Blood Sugar Levels
- Diabetes: Counting Carbs if You Don't Use Insulin
- Diabetes: Coping With Your Feelings About Your Diet
- Diabetes: Tracking My Feelings
- Diabetes: Taking Care of Your Feet
- Diabetes: Care of Blood Sugar Test Supplies
- Diabetes: Checking Your Blood Sugar
- Diabetes: Checking Your Feet
- Diabetes: Steps for Foot-Washing
- Diabetes: Protecting Your Feet
- Diabetes: Dealing With Low Blood Sugar From Medicines
- Diabetes: Dealing With Low Blood Sugar From Insulin or Medicine
- Diabetes: How to Give Glucagon
- Low Blood Sugar Level Record
- Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar
- Diabetes: Preventing High Blood Sugar Emergencies
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
- High Blood Sugar Level Record
- Symptoms of High Blood Sugar
- Diabetes: Using Canada's Food Guide
- Diabetes: Giving Yourself an Insulin Shot
- Glycemic Index
- Diabetes and Alcohol
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring
- Quick Tips: Diabetes and Shift Work
- Diabetes: How to Prepare for a Colonoscopy
- Type 2 Diabetes: Can You Cure It?
- Diabetes, Type 2: Should I Take Insulin?
- Prediabetes: Which Treatment Should I Use to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes?
- Diabetes: Making Medical Decisions as Your Health Changes
- Diabetes Care Plan
- Diabetes: Caregiving for an Older Adult
- Quick Tips: Smart Snacking When You Have Diabetes
- Testing Tips From a Diabetes Educator
- Gloria's Story: Adding Activity to Help Control Blood Sugar
- Andy's Story: Finding Your Own Routine When You Have Diabetes
- Jerry's Story: Take Prediabetes Seriously
- Linda's Story: Getting Active When You Have Prediabetes
- Diabetes
- Tips for Exercising Safely When You Have Diabetes
- Diabetes: Travel Tips
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Care of Your Skin When You Have Diabetes
- Diabetes: Taking Care of Your Teeth and Gums
- Non-insulin medicines for type 2 diabetes
- Metformin for diabetes
- Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar) in People Without Diabetes
- Diabetic Retinopathy
- Laser Photocoagulation for Diabetic Retinopathy
- Diabetic Neuropathy
- Diabetic Atypical Neuropathies
- Diabetic Neuropathy: Exercising Safely
- Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy
- Criteria for Diagnosing Diabetes
- Diabetes-Related High and Low Blood Sugar Levels
- Diabetic Nephropathy
- Diabetes: Cholesterol Levels
- Diabetes and Infections
- Diabetes: Tests to Watch for Complications
- Diabetes: Differences Between Type 1 and 2
- Diabetes Complications
- How Diabetes Causes Blindness
- How Diabetes Causes Foot Problems
- Reading Food Labels When You Have Diabetes
- Eating Out When You Have Diabetes
- Breastfeeding When You Have Diabetes
- Diabetes: Staying Motivated
- Sick-Day Guidelines for People With Diabetes
- Diabetes: Amputation for Foot Problems
- Prediabetes
- Prediabetes: Exercise Tips
- Type 2 Diabetes: Screening for Adults
- Diabetes: Should I Get an Insulin Pump?
- Diabetes: Living With an Insulin Pump
- Form for Carbohydrate Counting
-
Disease and Disease Prevention
- Diseases and Conditions
- Osgood-Schlatter Disease
- Needle Aponeurotomy for Dupuytren's Disease
- Mitochondrial Diseases
- Disease and Injury Prevention
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Root Planing and Scaling for Gum Disease
- Kawasaki Disease
- Tay-Sachs Disease
- Von Willebrand's Disease
- Hirschsprung's Disease
- Complications of Paget's Disease
- Paget's Disease of Bone
- Celiac Disease
- Peptic Ulcer Disease
- Ménière's Disease
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: Tubo-Ovarian Abscess
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Addison's Disease
- Misdiagnosis of Lyme Disease
- Lyme Disease
- Parkinson's Disease and Freezing
- Parkinson's Disease: Other Symptoms
- Parkinson's Disease: Modifying Your Activities and Your Home
- Parkinson's Disease and Tremors
- Parkinson's Disease and Speech Problems
- Parkinson's Disease
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
- Parkinson's Disease: Movement Problems From Levodopa
- Mad Cow Disease
- Handwashing
- Peyronie's Disease
- Stages of Lyme Disease
- Osteotomy and Paget's Disease
- Dupuytren's Disease
- Crohn's Disease
- Crohn's Disease: Problems Outside the Digestive Tract
- Pilonidal Disease
- Acquired Von Willebrand's Disease
-
Down Syndrome, Autism and Developmental Delays
- Autism
- Down Syndrome: Helping Your Child Eat Independently
- Down Syndrome: Grooming and Hygiene
- Down Syndrome: Helping Your Child Learn to Walk and Use Other Motor Skills
- Down Syndrome: Helping Your Child Learn to Communicate
- Down Syndrome
- Dyslexia
- Conditions Related to Dyslexia
- Autism: Behavioural Training and Management
- Autism: Support and Training for the Family
- Unproven Treatments for Autism
- Caring for Adults With Autism
- Down Syndrome: Helping Your Child Avoid Social Problems
- Down Syndrome: Training and Therapy for Young People
- Down Syndrome: Helping Your Child Dress Independently
- Down Syndrome, Ages Birth to 1 Month
- Down Syndrome, Ages 1 Month to 1 Year
- Down Syndrome, Ages 1 to 5
- Down Syndrome, Ages 5 to 13
- Down Syndrome, Ages 13 to 21
- Eating Disorders
-
Epilepsy
- Absence Epilepsy
- Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy
- Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
- Focal Epilepsy
- Epilepsy: Focal Aware Seizures
- Epilepsy
- Epilepsy and Driving
- Epilepsy: Generalized Seizures
- Epilepsy: Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
- Epilepsy: Myoclonic Seizures
- Epilepsy: Atonic Seizures
- Epilepsy: Tonic Seizures
- Epilepsy: Focal Impaired Awareness Seizures
- Epilepsy Medicine Therapy Failure
- Stopping Medicine for Epilepsy
- Questions About Medicines for Epilepsy
- Epilepsy: Taking Your Medicines Properly
-
Fatigue and Sleep
- Sleep Apnea: Should I Have a Sleep Study?
- Sleep and Your Health
- Quick Tips: Making the Best of Shift Work
- Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Managing Your Energy
- Sleeping Better
- Sleep Problems
- Doxepin (Sleep) - Oral
- Improving Sleep When You Have Chronic Pain
- Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
- Chronic Fatigue: Changing Your Schedule
- Chronic Fatigue: Getting Support
- Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Coping With Changing Sleep Patterns as You Get Older
- Stages of Sleep
- Sleep Apnea: Fibre-Optic Pharyngoscopy
- Oral Breathing Devices for Sleep Apnea and Snoring
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Sleep Apnea
- Sleep Problems, Age 12 and Older
- Stages of Sleep Apnea
- Sleep Journal
- Shift Work Sleep Disorder
- Snoring
- Sleep Problems: Dealing With Jet Lag
- Insomnia
- Sleep and Your Body Clock
- Weakness and Fatigue
- Insomnia: Improving Your Sleep
-
Heart Health and Stroke
- Peripheral Arterial Disease
- Bradycardia (Slow Heart Rate)
- Types of Bradycardia
- Cardiac Device Monitoring
- Angioplasty for Peripheral Arterial Disease of the Legs
- Isolated Systolic High Blood Pressure
- Atrial Fibrillation: Should I Try Electrical Cardioversion?
- Change in Heartbeat
- Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Fast Heart Rate
- Heart Failure: Symptom Record
- Heart Failure: Compensation by the Heart and Body
- Heart Failure: Taking Medicines Properly
- Heart Failure: Watching Your Fluids
- Heart Failure: Avoiding Triggers for Sudden Heart Failure
- Heart Failure: Activity and Exercise
- Heart Tests: When Do You Need Them?
- Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)
- Cardiac Arrest
- Heart Failure Daily Action Plan
- Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)
- Heart Rate Problems: Should I Get a Pacemaker?
- Heart Rhythm Problems: Should I Get an Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD)?
- What to Do if Your Cardiac Device Is Recalled
- Venous Insufficiency
- Carotid Artery Stenting
- ICD: Living Well With It
- Diabetes: Lower Your Risk for Heart Attack and Stroke
- Pacemaker for Heart Failure (Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy)
- Heart Attack: How to Prevent Another One
- Stroke: How to Prevent Another One
- Sex and Your Heart
- Supraventricular Tachycardia: Should I Have Catheter Ablation?
- Carotid Artery Disease
- Giant Cell Arteritis
- High Blood Pressure: Over-the-Counter Medicines to Avoid
- Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)
- Leg Aneurysm
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH)
- Heart Failure: Checking Your Weight
- Alan's Story: Coping With Change After a Heart Attack
- Quick Tips: Taking Charge of Your Angina
- Heart and Circulation
- High Blood Pressure
- Heartburn
- Angioplasty for Coronary Artery Disease
- Coronary Artery Disease
- Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD)
- Aortic Valve Regurgitation
- Aortic Valve Stenosis
- Secondary High Blood Pressure
- Hemorrhagic Stroke
- Stroke: Common Problems
- Self-Care After a Stroke
- Stroke: Dealing With Depression
- Stroke: Getting Dressed
- Stroke: Speech and Language Problems
- Stroke: Bladder and Bowel Problems
- Stroke: Preventing Injury in Affected Limbs
- After a Stroke: Helping Your Family Adjust
- Stroke: Behaviour Changes
- Stroke: Changes in Emotions
- Stroke: Perception Changes
- Stroke: Problems With Ignoring the Affected Side
- Stroke: Memory Tips
- Stroke: Your Rehabilitation Team
- Stroke
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Lifestyle Changes
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Hospital Program
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Home Program
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Outpatient Program
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Maintenance Program
- Congenital Heart Defects
- Congenital Heart Disease: Caring for Your Child
- Coronary Artery Disease: Should I Have an Angiogram?
- Sudden Heart Failure
- Classification of Heart Failure
- Heart Failure: Tips for Easier Breathing
- Heart Failure: Avoiding Colds and Flu
- Heart Failure
- Helping Someone During a Panic Attack
- Aortic Aneurysm
- High Blood Pressure
- Coronary Artery Disease: Family History
- Angina
- Using Nitroglycerin for Angina
- Heartburn: Changing Your Eating Habits
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)
- Beta-blockers
- Heart Rhythm Problems: Diary of Symptoms
- Vagal Manoeuvres for Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
- Electrical Cardioversion (Defibrillation) for a Fast Heart Rate
- Catheter Ablation for a Fast Heart Rate
- Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Home Blood Pressure Log
- Blood Pressure Screening
- Heart Block
- Electrical System of the Heart
- Heart Rhythm Problems and Driving
- Heart Rhythm Problems: Symptoms
- Resuming Sexual Activity After a Heart Attack
- Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease
- Pacemaker for Bradycardia
- SPECT Image of the Heart
- Heart Attack and Stroke in Women: Reducing Your Risk
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Aspirin to Prevent Heart Attack and Stroke
- Temporal Artery Biopsy
- Emergency First Aid for Heatstroke
- Heartburn Symptom Record
- Heart Attack and Unstable Angina
- Congenital Heart Disease in Adults
- Monitoring and Medicines for Heart Failure
- Ventricular Assist Device (VAD) for Heart Failure
- Cardiac Output
- Heart Failure Symptoms
- Heart Failure: Less Common Symptoms
- Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction (Systolic Heart Failure)
- Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction (Diastolic Heart Failure)
- High-Output Heart Failure
- Right-Sided Heart Failure
- Heart Failure Complications
- How the Heart Works
- Coronary Arteries and Heart Function
- Heart Failure Types
- Enjoying Life When You Have Heart Failure
- Heart Failure: Tips for Caregivers
- Medicines to Prevent Abnormal Heart Rhythm in Heart Failure
- Cardiac Cachexia
- Heart Failure Stages
- Cardiac Rehabilitation Team
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Emotional Health Benefits
- Ischemia
- Coronary Artery Disease: Roles of Different Doctors
- Coronary Artery Disease: Helping a Loved One
- Manage Stress for Your Heart
- Intermittent Claudication
- Peripheral Arterial Disease: Pulse and Blood Pressure Measurement
- Heart Failure and Sexual Activity
- Joan's Story: Coping With Depression and Anxiety From Heart Failure
- Rheumatic Fever and the Heart
- Acute Coronary Syndrome
- Aspirin: Should I Take Daily Aspirin to Prevent a Heart Attack or Stroke?
- Heart Failure: Should I Get a Pacemaker ?
- Heart Failure: Should I Get an Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD)?
- Heart Valve Disease
- Myxoma Tumours of the Heart
- Aortic Dissection
- Heart Attack and Stroke Risk Screening
- High Blood Pressure: Checking Your Blood Pressure at Home
- Hypertensive Emergency
- Stroke Rehabilitation
- Treatment for Stroke-Related Spasticity
- Driving a Car After a Stroke
- Heart Failure: Avoiding Medicines That Make Symptoms Worse
- Stroke Recovery: Coping With Eating Problems
- Heart Murmur
- Coronary Artery Disease: Should I Have Angioplasty for Stable Angina?
- Tyrell's Story: Taking Pills for High Blood Pressure
- Stroke Prevention: Should I Have a Carotid Artery Procedure?
- Atrial Fibrillation: Which Anticoagulant Should I Take to Prevent Stroke?
- Atrial Fibrillation: Should I Take an Anticoagulant to Prevent Stroke?
- Smoking and Coronary Artery Disease
-
Hepatitis
- Hepatitis C: Your Risk for Cirrhosis
- Hepatitis E
- Hepatitis B Immune Globulin - Injection
- Heparin - Injection
- Fulminant Hepatitis
- Protect Yourself From Hepatitis A When Travelling
- Hepatitis A
- Viral Hepatitis
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis D
- Hepatitis B: How to Avoid Spreading the Virus
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis Panel
- Hepatitis B Treatment Recommendations
-
HIV
- HIV Infection
- HIV Viral Load
- HIV: Stages of Infection
- Ways HIV Cannot Be Spread
- HIV and Exercise
- HIV: Giving Support
- HIV: Tips for Caregivers to Avoid Infection
- HIV: Preventing Other Infections When You Have HIV
- HIV Home Care
- Antiretroviral medicines for HIV
- Resistance to HIV Medicines
- HIV: Preventing Infections
- HIV: Antiretroviral Therapy (ART)
- Opportunistic Infections in HIV
- HIV: Taking Antiretroviral Medicines
- HIV: Non-Progressors and HIV-Resistant People
- HIV Screening
- HIV and Weight Loss
- HIV and Fatigue
-
Infectious Diseases
- Anthrax
- Avian Influenza
- Avoiding Infections in the Hospital
- Bacterial Infections of the Spine
- Bites and Stings: Flu-Like Symptoms
- Boric Acid for Vaginal Yeast Infection
- Caregiving: Reducing Germs and Infection in the Home
- Central Vascular Access Device (CVAD): Flushing
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Chickenpox: Preventing Skin Infections
- Chikungunya Fever
- Complicated Urinary Tract Infections
- Complications of Ear Infections
- Cranberry Juice and Urinary Tract Infections
- Dengue Fever
- Ear Infection: Should I Give My Child Antibiotics?
- Ear Infections
- Ebola or Marburg Virus Infection
- Ebola Virus Disease
- Enterovirus D68 (EV-D68)
- Fever or Chills, Age 11 and Younger
- Fever or Chills, Age 12 and Older
- Fever Seizures
- Feverfew for Migraines
- Fifth Disease
- Flu: Signs of Bacterial Infection
- Fungal Nail Infections
- Giardiasis
- Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease
- Kissing Bugs
- Measles (Rubeola)
- Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)
- Molluscum Contagiosum
- Mpox
- Mononucleosis (Mono)
- Mononucleosis Complications
- Mumps
- Neutropenia: Preventing Infections
- Non-Surgical Nail Removal for Fungal Nail Infections
- Noroviruses
- Pleurisy
- Pneumonia
- Preventing Tetanus Infections
- Pseudomonas Infection
- Recurrent Ear Infections and Persistent Effusion
- Recurrent Vaginal Yeast Infections
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Infection
- Rotavirus
- Rubella (German Measles)
- Scarlet Fever
- Sexually Transmitted Infections
- Sexually Transmitted Infections: Genital Examination for Men
- Sexually Transmitted Infections: Symptoms in Women
- Sexually Transmitted Infections: Treatment
- Shingles
- Smallpox
- Sore Throat and Other Throat Problems
- Staph Infection
- Strep Throat
- Symptoms of Pelvic Infection
- Thrush
- Tick Bites: Flu-Like Symptoms
- Tinea Versicolor
- Tuberculosis (TB)
- Tuberculosis (TB) Screening
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Risks for Older Adults
- Vaginal Yeast Infections
- Valley Fever
- West Nile Virus
- Zika Virus
- Informed Health Decisions
-
Injuries
- Trapped Finger, Toe, or Limb
- Blister Care
- Exercises for Heel Pain or Tightness
- Broken Toe
- Broken Nose (Nasal Fracture)
- Preventing Blisters
- Hip Fracture
- Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injury
- Pressure Injuries From Scuba Diving
- Pressure Injuries: Stages
- Pressure Injuries: Prevention and Treatment
- Calf Muscle Injury
- Avulsion Fracture
- Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Injury
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Injury
- Frozen or Stuck Tongue or Other Body Part
- Jones Fracture
- Animal and Human Bites
- Blisters
- Burns and Electric Shock
- Choking Rescue Procedure: Heimlich Manoeuvre
- Cold Temperature Exposure
- Cuts
- Ear Problems and Injuries, Age 11 and Younger
- Elbow Injuries
- Elbow Problems, Non-Injury
- Facial Injuries
- Facial Problems, Non-Injury
- Fish Hook Injuries
- Toe, Foot, and Ankle Injuries
- Groin Problems and Injuries
- Finger, Hand, and Wrist Injuries
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries
- Safe Hand and Wrist Movements
- Physical Rehabilitation for ACL Injuries
- Marine Stings and Scrapes
- Mouth Problems, Non-Injury
- Nail Problems and Injuries
- Puncture Wounds
- Shoulder Problems and Injuries
- Removing Splinters
- Swallowed Button Disc Battery, Magnet, or Object With Lead
- Object Stuck in the Throat
- How a Scrape Heals
- Removing an Object From a Wound
- Types of Chest Injuries
- Injury to the Tailbone (Coccyx)
- First Aid for a Spinal Injury
- Body Mechanics
- Scrapes
- Swallowed or Inhaled Objects
- Swelling
- Overuse Injuries
- Meniscus Tear
- Razor Bumps
- Ankle Sprain
- Sprained Ankle: Using a Compression Wrap
- High-Pressure Injection Wounds
- Patellar Dislocation
- Hamstring Muscles
- Plica in the Knee
- Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis
- Pressure Injuries
- Heat After an Injury
- Concussion
- Navicular (Scaphoid) Fracture of the Wrist
- Cold Exposure: What Increases Your Risk of Injury?
- Broken Collarbone
- Shoulder Separation
- Frozen Shoulder
- Preventing ACL Injuries
- Living With a Spinal Cord Injury
- Classification of Spinal Cord Injuries
- Tendon Injury (Tendinopathy)
- Shin Splints
- Muscle Cramps
- Whiplash
- Broken Rib
-
Joints and Spinal Conditions
- Osteochondritis Dissecans of a Joint
- Returning to Work With Low Back Pain
- Moving From Sitting to Standing
- Golfer's Elbow
- Bones, Joints, and Muscles
- Hip Injuries, Age 11 and Younger
- Hip Injuries, Age 12 and Older
- Hip Problems, Age 12 and Older
- Rotator Cuff Disorders
- Osteoporosis
- Spina Bifida
- Temporomandibular Disorders: Having Good Body Mechanics
- Temporomandibular Disorders (TMD)
- Tennis Elbow
- Debridement for Rotator Cuff Disorders
- Spinal Curves in Scoliosis
- Spondyloarthropathies
- Knee Problems and Injuries
- Posture: Standing and Walking
- Osteoporosis Risk Factors
- Bruxism and Temporomandibular Disorders
- Patellar Subluxation
- Steroid-Induced Osteoporosis
- Cervical Spinal Stenosis
- Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- Spasticity
- Scoliosis In Adults
- Acute Flaccid Myelitis
- Spinal Cord Injury: Abdominal Thrust Assist (Assisted Cough)
- Spinal Cord Injury: Your Rehabilitation Team
- Spinal Cord Injury: Talking With Your Partner About Sex
- Mobility After a Spinal Cord Injury
- Spinal Cord Injury: Adapting Your Home
- Spinal Cord Injury: Safe Transfers To or From a Wheelchair
- Spinal Cord Injury: Autonomic Dysreflexia
- Back Problems and Injuries
- Proper Sitting for a Healthy Back
- Brace (Orthotic) Treatment for Scoliosis
- Proper Back Posture (Neutral Spine)
- Severity of Back Injuries
- Back Problems: Proper Lifting
- Degenerative Disc Disease
-
Kidneys
- Acute Kidney Injury Versus Chronic Kidney Disease
- Nephrotic Syndrome
- Uremia
- Kidney Stones: Should I Have Lithotripsy to Break Up the Stone?
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- Kidney Failure: Should I Start Dialysis?
- Anemia of Chronic Kidney Disease
- End-Stage Kidney Failure
- Tolvaptan (Inherited Kidney Disease) - Oral
- Types of Kidney Stones
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) for Kidney Stones
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy or Nephrolithotripsy for Kidney Stones
- Kidney Stones
- Advance Care Planning: Should I Stop Kidney Dialysis?
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Medicines to Be Careful With
- Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease
- Medicines That Can Cause Acute Kidney Injury
- Donating a Kidney
-
Lung and Respiratory Conditions
- Breathing Problems: Using a Metered-Dose Inhaler
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
- Bronchiectasis
- Chest Problems
- Sildenafil 20 Mg (Lungs) - Oral
- Tadalafil (Lungs) - Oral
- Tests for Lung Infections
- COPD: Lung Volume Reduction Surgery
- Acute Bronchitis
- Respiratory Problems, Age 11 and Younger
- Respiratory Problems, Age 12 and Older
- Breathing Smoke or Fumes
- Pulmonary (Lung) Nodules
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)
- COPD's Effect on the Lungs
- Black Lung Disease
- Oral Breathing Devices for Snoring
- Spinal Cord Injury: Breathing Practice
- Breathing Problems: Using a Dry Powder Inhaler
- COPD: Clearing Your Lungs
- Collapsed Lung (Pneumothorax)
- Interactive Tool: Should I Consider Surgery for My Low Back Problem?
- Lung Problems: Learning to Breathe Easier
- Lung Function in COPD
- COPD: Handling a Flare-Up
- Sarah's Story: Dealing With the Emotions From COPD
- Fran's Story: Finding Support When You Have COPD
-
Multiple Sclerosis
- Multiple Sclerosis: Alternative Treatments
- Multiple Sclerosis: Modifying Your Home
- Multiple Sclerosis: Bladder Problems
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Types of Multiple Sclerosis
- Multiple Sclerosis Progression
- Multiple Sclerosis: MRI Results
- Multiple Sclerosis: Mental and Emotional Problems
- Multiple Sclerosis: Questions About What to Expect
- Rehabilitation Programs for Multiple Sclerosis
- Obesity
-
Rehabilitation and Exercise
- Breathing Exercises: Using a Manual Incentive Spirometer
- Sensual Exercises for Erection Problems
- Breastfeeding: Exercise and Weight Loss
- Jaw Problems: Exercise and Relaxation
- Exercises for Arm and Wrist
- Kegel Exercises
- Tennis Elbow: Stretches and Strengthening Exercises
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Exercise
- Neck Exercises
- Stress Management: Imagery Exercises
- Sprained Ankle: Rehabilitation Exercises
- Plantar Fasciitis: Exercises to Relieve Pain
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Medicine and Exercise
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Monitoring Your Body's Response to Exercise
- Rotator Cuff Problems: Exercises You Can Do at Home
- Stress Management: Breathing Exercises
- ACL Injury: Exercises to Do Before Treatment
- Spinal Cord Injury: Sensual Exercises
- Martha's Story: A Voice for Recovery
- Stan's Story: Getting There Hasn't Been Easy
- Debbie's Story: People Can and Do Recover
- Susan's Story: A Friend Really Helps
- Meniscus Tear: Rehabilitation Exercises
- Patellar Tracking Disorder: Exercises
- Stress Management: Breathing Exercises for Relaxation
- Good-Health Attitude
-
Sexual, Reproductive Health
- Menopause: Should I Use Hormone Therapy (HT)?
- Gender Identity Issues: Getting Support
- Heavy Menstrual Periods
- Pubic Lice
- Menopause and Your Risk for Other Health Concerns
- Menstrual Cups
- Gender Dysphoria
- Menstrual Cramps: Relieving Pain
- Men's Health
- Sexual and Reproductive Organs
- Sexual Health
- Women's Health
- Genital Warts
- Sexuality While Breastfeeding
- Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
- Chlamydia
- Sexuality and Physical Changes With Aging
- Relieving Menstrual Pain
- Uterine Fibroids
- Gonorrhea
- Syphilis
- Neurosyphilis
- Congenital Syphilis
- Emotions and Menopause
- Hot Flashes and Menopause
- Vaginal Dryness
- Genital Herpes
- Parkinson's Disease and Sexual Problems
- Male Genital Problems and Injuries
- Menstrual Cramps
- Missed or Irregular Periods
- Genital Self-Examination
- Missed Periods and Endurance Training
- Rashes or Sores in the Groin
- Other Health Problems Caused by Herpes Simplex Virus
- Arrhythmias and Sexual Activity
- Stages of Syphilis
- Normal Vaginal Discharge
- Vaginal Rashes and Sores
- Vaginal Fistula
- Soy for Menopause Symptoms
- Menopause: Wild Yam and Progesterone Creams
- Normal Menstrual Cycle
- Vaginal Pessaries
- Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
- Uterine Fibroids: Should I Use GnRH-A Therapy?
- Uterine Fibroids: Should I Have Uterine Fibroid Embolization?
- Menopause: Managing Hot Flashes
- Premature Ejaculation
- High-Risk Sexual Behaviour
- Object in the Vagina
- Periodic Limb Movement Disorder
- Military Sexual Trauma
- Sexual Problems in Women
- Female Genital Problems and Injuries
- Smoking: Sexual and Reproductive Problems
-
Skin, Nails and Rashes
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Removing Moles and Skin Tags
- Caregiving: Skin Care for Immobile Adults
- Yeast Skin Infection
- Bruises and Blood Spots Under the Skin
- Skin, Hair, and Nails
- Nail Psoriasis
- Phototherapy for Psoriasis
- Psoriasis
- Ringworm of the Skin
- Rash, Age 12 and Older
- Sunburn: Skin Types
- Heat Rash
- Colour Changes in Nails
- Changes in Your Nails
- Cut That Removes All Layers of Skin
- Skin Changes
- Venous Skin Ulcer
- Venous Skin Ulcers: Home Treatment
- Eczema: Taking Care of Your Skin
- Seborrheic Keratoses
- Care for a Skin Wound
- Psoriasis: Skin, Scalp, and Nail Care
- Protecting Your Skin From the Sun
- Skin Rashes: Home Treatment
- Skin Cyst: Home Treatment
- Calluses and Corns
- Calluses and Corns: Using Pumice Stones
- Calluses and Corns: Protective Padding
- Tazarotene (Psoriasis/Acne) - Topical
- Types of Acne
- Acne: Treatment With Benzoyl Peroxide
- Acne: Treatment With Alpha Hydroxy Acids
- Acne: Treatment With Salicylic Acid
- Acne: Treatment With Antibiotics
- Acne
- Acne: Tips for Keeping It Under Control
- Acne: Should I Take Isotretinoin for Severe Acne?
-
Thyroid
- Hyperthyroidism: Should I Use Antithyroid Medicine or Radioactive Iodine?
- Thyroid Storm
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Thyroid - Oral
- Subclinical Hypothyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism: Graves' Ophthalmopathy
- Radioactive Iodine for Hyperthyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism
- Thyroid Nodules
- Thyroid Hormone Production and Function
- Vertigo
- Check Your Symptoms
- Search Health Topics
Topic Overview
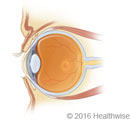
What is diabetic retinopathy?
Retinopathy is a disease of the retina. The retina is the nerve layer that lines the back of your eye. It is the part of your eye that "takes pictures" and sends the images to your brain. Many people with diabetes get retinopathy. This kind of retinopathy is called diabetic retinopathy (retinal disease caused by diabetes).
Diabetic retinopathy can lead to poor vision and even blindness. Most of the time, it gets worse over many years. At first, the blood vessels in the eye get weak. This can lead to blood and other liquid leaking into the retina from the blood vessels. This is called non-proliferative retinopathy. And this is the most common retinopathy. If the fluid leaks into the centre of your eye, you may have blurry vision. Most people with non-proliferative retinopathy have no symptoms.
If blood sugar levels stay high, diabetic retinopathy will keep getting worse. New blood vessels grow on the retina. This may sound good, but these new blood vessels are weak. They can break open very easily, even while you are sleeping. If they break open, blood can leak into the middle part of your eye in front of the retina and change your vision. This bleeding can also cause scar tissue to form, which can pull on the retina and cause the retina to move away from the wall of the eye (retinal detachment). This is called proliferative retinopathy. Sometimes people don't have symptoms until it is too late to treat them. This is why having eye examinations regularly is so important.
Retinopathy can also cause swelling of the macula of the eye. This is called macular edema. The macula is the middle of the retina, which lets you see details. When it swells, it can make your vision much worse. It can even cause legal blindness.
What causes diabetic retinopathy?
If you are not able to keep your blood sugar levels in a target range, it can cause damage to your blood vessels. Diabetic retinopathy happens when high blood sugar damages the tiny blood vessels of the retina.
When you have diabetic retinopathy, high blood pressure can make it worse. High blood pressure can cause more damage to the weakened vessels in your eye, leading to more leaking of fluid or blood and clouding more of your vision.
What are the symptoms?
Most of the time, there are no symptoms of diabetic retinopathy until it starts to change your vision. When this happens, diabetic retinopathy is already severe. Having your eyes checked regularly can find diabetic retinopathy early enough to treat it and help prevent vision loss.
If you notice problems with your vision, call an eye doctor (ophthalmologist) right away. Changes in vision can be a sign of severe damage to your eye. These changes can include floaters, pain in the eye, blurry vision, or new vision loss.
How is diabetic retinopathy diagnosed?
An eye examination by an eye specialist (ophthalmologist or optometrist) is the only way to detect diabetic retinopathy. Having a dilated eye examination regularly can help find retinopathy before it changes your vision. On your own, you may not notice symptoms until the disease becomes severe.
Can diabetic retinopathy be prevented?
You can lower your chance of damaging small blood vessels in the eye by keeping your blood sugar levels and blood pressure levels within a target range. If you smoke, quit. All of this reduces the risk of damage to the retina. It can also help slow down how quickly your retinopathy gets worse and can prevent future vision loss.
If you have a dilated eye examination regularly, you and your doctor can find diabetic retinopathy before it has a chance to get worse. For most people, this will mean an eye examination every year. Finding retinopathy early gives you a better chance of avoiding vision loss and blindness.
How is it treated?
Surgery, laser treatment, or medicine may help slow the vision loss caused by diabetic retinopathy. You may need to be treated more than once as the disease gets worse.
Cause
Diabetes damages small blood vessels throughout the body, leading to reduced blood flow. When these changes affect the tiny blood vessels in the eyes, diabetic retinopathy may occur.
In the early stage of diabetic retinopathy, tiny blood vessels in the eye weaken and develop small bulges that may burst and leak into the retina. Later, new fragile blood vessels grow on the surface of the retina. These blood vessels may break and bleed into the eye, clouding vision and causing scar tissue to form.
The scar tissue may pull on the retina, leading to retinal detachment. Retinal detachment occurs when the retina separates from the wall of the eye. This can lead to vision loss.
Symptoms
You may have diabetic retinopathy for a long time without noticing any symptoms. Typically, retinopathy does not cause noticeable symptoms until significant damage has occurred and complications have developed.
Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy and its complications may include:
- Blurred, double, or distorted vision or difficulty reading.
- Floaters or spots in your vision.
- Partial or total loss of vision or a shadow or veil across your field of vision.
- Pain, pressure, or constant redness of the eye.
What Happens
Diabetic retinopathy begins as a mild disease. During the early stage of the disease, the small blood vessels in the retina become weaker and develop small bulges called microaneurysms. These microaneurysms are the earliest signs of retinopathy and may appear a few years after the onset of diabetes. They may also burst and cause tiny blood spots (hemorrhages) on the retina. But they do not usually cause symptoms or affect vision. This is called non-proliferative retinopathy. At this stage, treatment is not required.
As retinopathy progresses, fluid and protein leak from the damaged blood vessels and cause the retina to swell. This may cause mild to severe vision loss, depending on which parts of the retina are affected. If the centre of the retina (macula) is affected, vision loss can be severe. Swelling and distortion of the macula (macular edema), which results from a buildup of fluid, is the most common complication of retinopathy. Macular edema treatment usually works to stop and sometimes reverse your loss of vision.
In some people, retinopathy gets worse over the course of several years and progresses to proliferative retinopathy. In these cases, reduced blood flow to the retina stimulates the growth (proliferation) of fragile new blood vessels on the surface of the retina. As the new blood vessels multiply, one or more complications may develop and damage the person's vision. These complications can include:
- The formation of scar tissue that pulls on the retina, which may lead to retinal detachment.
- Bleeding inside the eye (preretinal or vitreous hemorrhage).
- The growth of new blood vessels on the surface of the iris (rubeosis iridis), which eventually leads to a form of severe glaucoma called neovascular glaucoma.
Any of these later complications may cause severe, permanent vision loss.
What Increases Your Risk
Your risk for diabetic retinopathy depends largely on two things: how long you have had diabetes and whether or not you have kept good control of your blood sugar.
You can control some risk factors, which are things that may increase your risk for diabetic retinopathy and its complications. Risk factors that you can control include:
- Pregnancy. Women who have diabetes are at increased risk of developing retinopathy during pregnancy. In women who already have retinopathy when they become pregnant, the condition can become much worse during pregnancy.
- Consistently high blood sugar. High blood sugar levels increase your risk of retinopathy. Keeping your blood sugar levels in a target range can reduce your risk for diabetic retinopathy and can slow the progression of the disease if it has already started.
- High blood pressure. In general, people with diabetes who also have high blood pressure are more likely to develop complications that affect the blood vessels in the body, including those in the eyes.
- Delayed diagnosis and treatment. Getting a dilated eye examination will not prevent retinopathy. But it may reduce your risk of severe vision loss from complications of retinopathy. By detecting it early, you can get treatment that can prevent vision loss and delay the progression of the disease.
- Smoking. Although smoking has not been proved to increase the risk of retinopathy, smoking may make many of the other health problems faced by people with diabetes worse, including disease of the small blood vessels.
If you have type 2 diabetes and use the medicine rosiglitazone (Avandia, Avandamet) to treat your diabetes, you may have a higher risk for problems with the centre of the retina (the macula). Health Canada, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the makers of the drug have warned that taking this medicine could cause swelling in the macula, which is called macular edema.
When should you call your doctor?
Call your doctor now if you have diabetes and notice:
- New or sudden vision changes.
- Floaters in your field of vision. Floaters often appear as dark specks, globs, strings, or dots. A sudden shower of floaters may be a sign of a retinal detachment, which is a serious complication of diabetic retinopathy.
- A new visual defect, shadow, or curtain across part of your vision. This is another sign of retinal detachment.
- Eye pain or a feeling of pressure in your eye.
- New or sudden vision loss. Sudden partial or complete vision loss is a symptom of many disorders that can occur within or outside the eye, including retinal detachment or bleeding within the eye. Sudden vision loss is always a medical emergency.
Call your doctor for an appointment if:
- You have more and more trouble doing everyday tasks (like driving or reading) because of your eyesight.
Watchful waiting
Watchful waiting is not okay if you have diabetes and notice changes in your vision.
If you have type 2 diabetes, even if you don't have any symptoms of eye disease, you still need to have your eyes and vision checked regularly by an eye specialist (ophthalmologist or optometrist). If you wait until you have symptoms, it's more likely that complications and severe damage to the retina will have already happened. These may be harder to treat. You could end up with permanent vision loss.
If you have type 1 diabetes, are age 10 or older, and were diagnosed 5 or more years ago, you should have your eyes checked even if you don't have symptoms. If you wait until you have symptoms, it's more likely that complications and severe damage to the retina will have happened. These may be harder to treat. And the damage may be permanent.
Watchful waiting is not an option if you already have diabetic retinopathy but don't have symptoms or vision loss. You will need to go back to your ophthalmologist for frequent checkups (every few months in some cases) so that your doctor can closely monitor changes in your eyes. There is no cure for the disease. But treatment can slow its progression. Your ophthalmologist can tell you how often you need to be checked.
Examinations and Tests
Diabetic retinopathy can be detected during a dilated eye examination by an ophthalmologist or optometrist. An examination by your primary doctor, during which your eyes are not dilated, is not an adequate substitute for a full examination done by an ophthalmologist or optometrist. Eye examinations for people with diabetes can include:
- Visual acuity testing. Visual acuity testing measures the eye's ability to focus and to see details at near and far distances. It can help detect vision loss and other problems.
- Ophthalmoscopy and slit lamp examination. These tests allow your doctor to see the back of the eye and other structures within the eye. They may be used to detect clouding of the lens (cataract), changes in the retina, and other problems.
- Gonioscopy. Gonioscopy is used to find out whether the area where fluid drains out of your eye (called the drainage angle) is open or closed. This test is done if your doctor thinks you may have glaucoma, a group of eye diseases that can cause blindness by damaging the optic nerve.
- Tonometry. This test measures the pressure inside the eye, which is called intraocular pressure (IOP). It is used to help detect glaucoma. Diabetes can increase your risk of glaucoma.
Your doctor may also do a test called an optical coherence tomography (OCT) to check for fluid in your retina. Sometimes a fluorescein angiogram is done to check for and locate leaking blood vessels in the retina, especially if you have symptoms, such as blurred or distorted vision, that suggest damage to or swelling of the retina.
Fundus photography can track changes in the eye over time in people who have diabetic retinopathy and especially in those who have been treated for it. Fundus photography produces accurate pictures of the back of the eye (the fundus). An eye doctor can compare photographs taken at different times to watch the progression of the disease and find out how well treatment is working. But the photos do not take the place of a full eye examination.
Early detection
Early detection and treatment of diabetic retinopathy can help prevent vision loss. For people in whom diabetic retinopathy has not been diagnosed, Diabetes Canada recommends that screening be done based on the following guidelines:
- People with type 1 diabetes who are age 15 and older should have a dilated eye examination within 5 years after diabetes is diagnosed and then every year.footnote 1
- People with type 2 diabetes should have an examination as soon as diabetes is diagnosed and then every year. If your eye examination results are normal or you have a very small amount of retinopathy, your doctor may consider follow-up examinations every 1 to 2 years.footnote 1
- If you are diagnosed with retinopathy, you may need frequent eye examinations.
- Women who have type 1 or type 2 diabetes and who are planning to get pregnant should have an examination before getting pregnant, during the first 3 months (first trimester) of pregnancy, and within the first year after the baby is born. The eye doctor can decide whether you need further screening for retinopathy during pregnancy based on the results of the first-trimester examination.footnote 2
Note: Pregnant women who develop gestational diabetes are not at risk for diabetic retinopathy and do not need to be screened for it. (But women who develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy have a greater chance of developing type 2 diabetes later in life, which can put them at increased risk for retinopathy and other eye problems.)
People who have diabetes are also at increased risk for other eye diseases, including glaucoma and cataracts. Regular dilated eye examinations can help detect these diseases early and prevent or delay vision loss.
Treatment Overview
There is no cure for diabetic retinopathy. But laser treatment (photocoagulation) is usually very effective at preventing vision loss if it is done before the retina has been severely damaged. Surgical removal of the vitreous gel (vitrectomy) may also help improve vision if the retina has not been severely damaged. Sometimes injections of an anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) medicine or an anti-inflammatory medicine help to shrink new blood vessels in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Because symptoms may not develop until the disease becomes severe, early detection through regular screening is important. The earlier retinopathy is detected, the easier it is to treat and the more likely vision will be preserved.
You may need treatment for diabetic retinopathy if:
- It has affected the centre (macula) of the retina.
- Abnormal new blood vessels have started to appear.
- Your side (peripheral) vision has been severely damaged.
If the macula has been damaged by macular edema, anti-VEGF medicine, such as aflibercept or ranibizumab, may help. Steroids may be injected into the eye. Sometimes an implant, such as Iluvien, may be placed in the eye to release a small amount of corticosteroid over time. If the retina hasn't been severely damaged, laser treatment or vitrectomy may help with macular edema.
Surgical removal of the vitreous gel (vitrectomy) is done when there is bleeding (vitreous hemorrhage) or retinal detachment, which are rare in people with early-stage retinopathy. Vitrectomy is also done when severe scar tissue has formed.
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy is often very effective in preventing, delaying, or reducing vision loss. But it is not a cure for the disease. People who have been treated for diabetic retinopathy need to be monitored frequently by an eye doctor to check for new changes in their eyes. Many people with diabetic retinopathy need to be treated more than once as the condition gets worse.
Also, controlling your blood sugar levels is always important. This is true even if you have been treated for diabetic retinopathy and your eyes are better. In fact, good blood sugar control is especially important in this case so that you can help keep your retinopathy from getting worse.
People with diabetes who have any signs of retinopathy need to be examined as soon as possible by an ophthalmologist.
Prevention
There are steps you can take to reduce your chance of vision loss from diabetic retinopathy and its complications:
- Control your blood sugar levels. Keep blood sugar levels in a target range by eating a healthful diet, frequently monitoring your blood sugar levels, getting regular physical exercise, and taking insulin or medicines for type 2 diabetes if prescribed.
- Control your blood pressure. Retinopathy is more likely to progress to the severe form and macular edema is more likely to occur in people who have high blood pressure. It is not clear whether treating high blood pressure can directly affect long-term vision. But in general, keeping blood pressure levels in a target range can reduce the risk of many different complications of diabetes. For more information about how to control your blood pressure, see the topic High Blood Pressure.
- Have your eyes examined by an eye specialist (ophthalmologist or optometrist) every year. Screening for diabetic retinopathy and other eye problems will not prevent diabetic eye disease. But it can help you avoid vision loss by allowing for early detection and treatment.
- See an ophthalmologist if you have changes in your vision. Changes in vision—such as floaters, pain or pressure in the eye, blurry or double vision, or new vision loss—may be symptoms of serious damage to your retina. In most cases, the sooner the problem can be treated, the more effective the treatment will be.
The risk for severe retinopathy and vision loss may be even less if you:
- Don't smoke. Although smoking has not been proved to increase the risk of retinopathy, smoking may aggravate many of the other health problems faced by people with diabetes, including disease of the small blood vessels.
- Avoid hazardous activities. Certain physical activities, like weight lifting or some contact sports, may trigger bleeding in the eye through impact or increased pressure. Avoiding these activities when you have diabetic retinopathy can help reduce the risk of damage to your vision.
- Get adequate exercise. Exercise helps keep blood sugar levels in a target range, which can reduce the risk of vision damage from diabetic retinopathy. Talk to your doctor about what kinds of exercise are safe for you.
Surgery
Surgical treatment for diabetic retinopathy is removal of the vitreous gel (vitrectomy). Vitrectomy does not cure the disease. But it may improve vision in people who have developed bleeding into the vitreous gel (vitreous hemorrhage), retinal detachment, or severe scar tissue formation.
Unfortunately, by the time some people are diagnosed with retinopathy (especially late-stage retinopathy), it is often too late for vitrectomy to provide much benefit. Even with treatment, vision may continue to decline.
Early detection of retinopathy through dilated eye examinations can help you decide to have surgery when it is most effective.
What to think about
After a person has had most of the vitreous gel removed by vitrectomy, surgery to remove scar tissue or to repair a new retinal detachment may be needed.
Vitrectomy is usually done as an outpatient surgery.
Other Treatment
Laser treatment (photocoagulation) can be an effective treatment for diabetic retinopathy. But it does not cure the disease. It can prevent, delay, and sometimes reverse vision loss. Without either laser treatment or surgery, vision loss caused by diabetic retinopathy and its complications may get worse until blindness occurs. So early treatment is vital to slowing vision loss, which can happen quickly.
When diabetic retinopathy causes bleeding (hemorrhage) into the vitreous gel, extensive scar tissue formation, or retinal detachment, surgical removal of the vitreous gel (vitrectomy) may be needed before laser treatment is considered.
Unfortunately, by the time some people are diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy, it is often too late for treatment to provide much benefit. Even with treatment, vision will continue to decline.
Early detection of retinopathy through dilated eye examinations can provide the opportunity to have laser treatment when it is most effective.
Other treatment choices
Laser photocoagulation uses the heat from a laser to seal or destroy abnormal, leaking blood vessels in the retina. It can cause the abnormal, weak blood vessels to shrink.
Some anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) medicines, such as aflibercept and ranibizumab, can help treat macular edema from diabetic retinopathy.
What to think about
Pan-retinal laser treatment is used to treat several spots on the retina during one or, most often, two sessions. It reduces the risk of serious bleeding and the progression of severe proliferative retinopathy.
Laser photocoagulation can result in some loss of vision, because it destroys some of the nerve cells in the retina and can cause the abnormal blood vessels to go away. With pan-retinal photocoagulation, this most often affects the outside (peripheral) vision, because the laser is directed at that area. Your vision may be worse right after treatment. But vision loss caused by laser treatment is mild compared with the vision loss that may be caused by untreated retinopathy.
Related Information
References
Citations
- Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee, et al. (2018). Retinopathy. Canadian Journal of Diabetes, 42(Suppl 1): S210–S216. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2017.10.027. Accessed October 15, 2018.
- Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee, et al. (2018). Diabetes and pregnancy. Canadian Journal of Diabetes, 42(Suppl 1): S255–S282. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2017.10.038. Accessed October 15, 2018. [Erratum in Canadian Journal of Diabetes 42(3): 337. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2018.04.006.] Accessed October 12, 2018.
Other Works Consulted
- American Academy of Ophthalmology (2014). Diabetic retinopathy summary benchmark—2014 (Preferred Practice Pattern guidelines). http://one.aao.org/summary-benchmark-detail/diabetic-retinopathy-summary-benchmark--october-20. Accessed December 15, 2014.
- American Optometric Association (2014). Evidence-based clinical practice guideline: Eye care of the patient with diabetes mellitus. http://www.aoa.org/optometrists/tools-and-resources/clinical-care-publications/clinical-practice-guidelines?sso=y. Accessed December 15, 2014.
- Brownlee M, et al. (2011). Complications of diabetes mellitus. In S Melmed et al., eds., Williams Textbook of Endocrinology, 12th ed., pp. 1462–1551. Philadelphia: Saunders.
- Fletcher EC, et al. (2011). Retina. In P Riordan-Eva, JP Whitcher, eds., Vaughan and Asbury's General Ophthalmology, 18th ed., pp. 190–221. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Mohamed QA, et al. (2011). Diabetic retinopathy (treatment), search date June 2010. BMJ Clinical Evidence. Available online: http://www.clinicalevidence.com.
Credits
Current as of: March 1, 2023
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:
Adam Husney MD - Family Medicine
Donald Sproule MDCM, CCFP - Family Medicine
Kathleen Romito MD - Family Medicine
Carol L. Karp MD - Ophthalmology
Current as of: March 1, 2023
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:Adam Husney MD - Family Medicine & Donald Sproule MDCM, CCFP - Family Medicine & Kathleen Romito MD - Family Medicine & Carol L. Karp MD - Ophthalmology
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated.